Light
|
Light
Light waves , radio waves and X-Rays, and gamma rays are all types of electromagntic waves.
Luminous Flux = 4 . p luminous intensity.
Note : 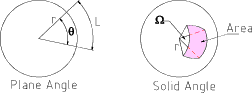
The flux of a 1 cd source results in a luminous intensity of 1 lumen/ steradian.
The definition of liminous flux is ;- Luminous Flux = F = I . Ω The illumination (E) of a surface is the liminous flux per unit area that reaches the surface. The unit of illumination is the lux (lx). Illumination E (lx) = F (lm) /A (m2) Reflection of LightWhen a beam of light is reflected from a reflective plane surface the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence. The image
has the same shape and size as the object but with left and right reversed. The image is perceived to be the same distance behind the mirror as
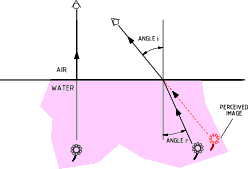
the object is in front. 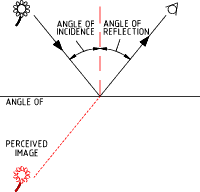 Refraction of Light The velocity of life is different in different mediums. When a beam of
light passes from one medium to another at an angle its direction changes.
The greater the differences in the velocity of light in the different mediums
the greater is the angle.
Index of refraction = n = c/v Snells Law = Sin i/Sin r = v1 / v2 = n2 / n1
The index of refraction varies with the frequency of light. White light comprises a number of
primary colours all of which have a different frequency. If light passes through a glass
object with parellel sides the light will bend as it enters one side of the and bend back on
leaving the object. If it passes through an object which does not have parallel
sides e.g a prism ,the light is effectively split into its primary colours.  If light passes from a medium of high refractive index to one of low refractive index e.g glass to air, there is an angle of incidence above which the angle of refraction is above 90o. Above this angle (critical angle) the light is reflected back into the into the original medium. This principle is used in the design of prisms used to bend light. 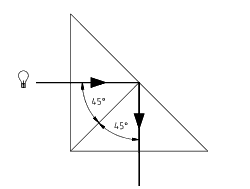 |
Sites Physics -Light
|
|