Introduction
This page simply identifies the panel products available, other than plywood.
This includse MDF (Medium density fibreboard),
wood particleboard,,oriented strand boards (OSB), and cement bonded particleboard.
Relevant Standards..For comprehensive list of standards Wood related Standards
BS 5268 -2 ;2002 Structural use of timber � Part 2: Code of practice for permissible
stress design, materials and workmanship.
BS 5268-2 ;2002 Structural use of timber � Part 2: Code of practice for permissible
stress design, materials and workmanship : section 5 deals with panel products other than plywood
BS EN 322:1993, Wood-based panels � Determination of moisture content.
BS EN 323:1993, Wood-based panels � Determination of density.
BS EN 324-1:1993, Wood-based panels � Determination of dimensions of boards � Part 1: Determination
of thickness, width and length.
BS EN 324-2:1993, Wood-based panels � Determination of dimensions of boards � Part 2: Determination
of squareness and edge straightness.
BS EN 622-2:2004, Fibreboards � Specifications � Part 2: Requirements for hardboards.
BS EN 622-3:2004, Fibreboards � Specifications � Part 3: Requirements for medium boards.
BS EN 622-5:2006, Fibreboards � Specifications � Part 5: Requirements for dry process boards (MDF).
BS EN 12369-1:2001, Wood-based panels � Characteristic values for use in structural design � Part 1: OSB,
particleboards and fibreboards.
BS EN 12369-2:2008, Wood-based panels � Characteristic values for structural design � Part 2: Plywood.
BS EN 12369-3:2008, Wood-based panels. Characteristic values for structural design. Solid-wood panels .
BS EN 12871, Wood-based panels � !Performance specifications and requirements for load bearing.
boards for use in floors, walls and roofs.
BS EN 312:Part 4::1997 Specification for cement bonded particleboard
DD ENV 12872, Wood-based panels � Guidance for structural panel installation.
Particle Board
Particleboard is cheaper and more uniform than conventional wood and plywood and is substituted for them
when appearance and strength are less important than cost.. It is weakest type of fibreboard, except for insulation board.
A major disadvantage of particleboard is that it is very prone to expansion and discoloration due to moisture, particularly
when it is not covered with paint or another sealer. Therefore, it is rarely used outdoors or for indoors areas which have high
moisture conditions. It is generally used for low cost bedroom and kitchen furniture as panels with external surfaces convered
with decorative layers of vinyl, melamine.
Particle board has little value as a structural material being greatly inferior to timber
MDF (Medium Density FibreBoard)
There are different types fibreboard which differentiated by
..the size and type of wood fibres used
..the method of heating
..what type of bonding agent is used
..the method by which it is pressed into shape
Medium Density Fibreboard (MDF) is a wood substitute form which is made from fine
wood fibres in a resin which is bonded under heat and pressure. It is
manufactured by a dry process at a lower temperature than other fibreboards e.g
hardboard. The natural glues and resins contained within the wood are not
effective. MDF therefore uses artificial bonding agents / resins.
The resin used is usually urea formaldehyde, but some fibreboard including exterior
or marine quality board will use stronger glues such as phenol formaldehyde.
MDF may be used instead of plywood or chipboard. It is dense, flat, stiff,
has no knots and is easily machined. It is made up of fine particles
and therefore does not have an easily recognisable surface grain
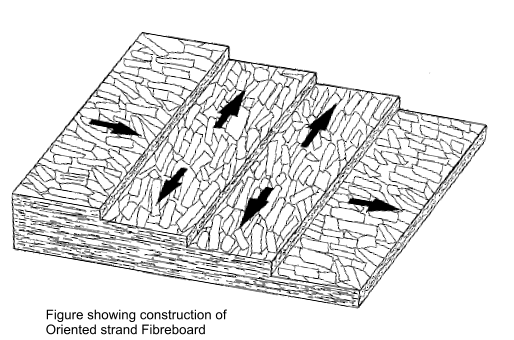
Oriented Strand Fibreboard
This is a panel material which is based of fibreboard with the fibres oriented in layers. This panel material is cheaper
and more easily produced than plywood, which requires large timber sections. It has slightly inferior properties compared to plywood
and is very suitable as an available low cost replacement.
This material can be used for structural and non-structural applications.
It is extensively used for wall sheaving and floor panels.
Cement Bonded particle Board
A bonded cement particle board panel is mad up of a mixture of wood particles and Portland cement together with some
additives. The panel is that it is grey in colour, has a
smooth surface and is heavy. The panel has the following advantageous properties
It is structurally strong, with good mechanical properties.
It is Fire resistant
It is non- combustible
It is resistant to fungal attack
It is Resistant to weather, freeze/thaw & standing water
It is resistant to Termite/Vermin Resistant:
It has good acoustic properties as a result of it high density
Cna be workded with standard carpentry tools and equipment
Is dimensionally stable when exposed to variations in temperature and moisture
Workability: Installs quickly using standard carpentry tools and equipment
It is an environmentally friendly building material
Because of its lay up, composition and mass, CBPB is mainly used for specialised
applications in construction. Its advantageous features with respect to
fire, durability, sound insulation and stiffness,make the product most suitable for internal
wall construction in public places, lining of lift shafts, construction of cabling ducts, soffits,
motorway acoustic fencing and cladding of prefabricated house units.
|
