Thermos Index Thermodynamics Condensers
|
Introduction A condenser in its simplest terms is a heat transfer device which reduces a
thermodynamic fluid from its vapor phase to its liquid phase. The main
use of a condenser is to receive exhausted steam from a steam engine or turbine and condense
the steam. The benefit being that the energy which would be exhausted to the
atmosphere is utilised and the engine turbine exhaust conditions are stable and controllable.
Condenser Types
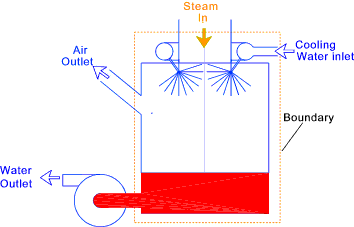
There are two principal types of condensers the jet condenser which employs a jet
of cold water to condense the steam and a surface condenser which employs cold metal
surfaces. The surface condenser is used for the majority of steam engine
& steam turbine applications... The principle elements of a jet condenser are shown in the figure below..
This type of condenser is suitable where conditions permit condensation of exhaust steam
by direct contact with the cooling water. It can maintain a pressure of less than
0,07 bara and can condense over 12000 kg/hr of steam. The vacuum is created in the
chamber by an air ejector. The cooling water is sprayed into the chamber an the fine spray
contacts the steam. The steam condenses and falls to the bottom of the condenser chamber
with the injection water. The condensed steam and injection water is withdrawn using
a centrifugal extraction pump. The jet condenser is generally provided with safety
features to guard against flooding m s (h - h d ) = m w (t o - t i ) + r = m sx h fg + m s(t sat- t d ) = mw (to - t i ) + r Thus, neglecting radiation, the ratio of the mass of jet water to the mass of steam condensed is :
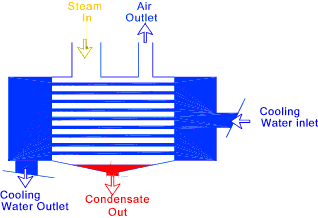
These notes do not include consideration of the air/gas removal system..... Surface Condenser The surface condenser is the most important type of condenser in present day use. Its main functions are to condense low pressure steam exhausted from turbines and also to maintain the vacuum at the exhaust end of the turbines. It has the advantage that the condensate and the cooling water are entirely separate. The condensate is thus delivered to the boiler feed system as distilled water and is at a higher temperature compared to the discharge of in jet condenser... The principle elements of a jet condenser are shown in the figure below.. This type of condenser has a large area of cooling surfaces compared to the system volume. The steam passes through the condenser and condenser on contact with the cooling surfaces. The condensate collects in the bottom of the condenser from where it is pumped away to the boiler feed system...
The heat transfer process in the condenser is such that the energy lost by the steam = the energy gained by the water... m s[ x h fg + (t sat- t c) ]) = mw (to - t i ) + r Thus the ratio of the mass of cooling water to the mass of steam condensed is :
....More notes to follow.... |
Thermodynamic Condensers
|
|
Thermos Index