Introduction
Many mechanical joints are totally depended on screws and bolts. This method allows
repeated assembly and disassembly with reliability and confidence. The screws and bolts are generally
low cost items with known strength and when used with nuts with similar rating provide highly engineered connections.
However when the connections are based on screws tightened into tapped holes there is more need to analyse the
strength of the joints.
The preferable failure mode for a screwed connection based on tapped holes is clearly failure of the screw. This is a replaceable
item and a failure is clearly detectable. The primary risk event is probably in the preloading operation where the screw may by tighted
to 70-80% of its yield strength.. A screw failure in this operation is not too serious an event.
If the screw is highly loaded e.g preloaded and is screwed into a material of lower strength than the screw then
a detailed assessment of the joint must be carried out to ensure that thread stripping will not occur..
Unfortunately the option of increasing the depth of the tapped hole is of limited value as it has been established that
there is no advantage if having a thread engagement in excess of the nominal screw diameter. The problem
is that the load taken by the screw is not evenly distributed. The majority of the load is taked by the first thread
and very little of the load is taken by the fourth thread onwards.
The preferred options are to design the joint to based on the use of suitably rated nuts or ensure the screw and parent
metalof the female thread,have similar mechanical strengths.
When the design is based on highly loaded /high strength screws fastened into threaded holes in components with lower strengths
then it may be necessary to use thread inserts.
Types of Thread Inserts
Helical Wire Inserts (Heli-Coil)
The helical wire inserts inserts, generally identified by the tradename Heli-coil, are made from diamond shaped wire formed into coils.
They are screwed into tapped holes such that the resulting internal profile of the coil is that of the desired female thread. The tapped
hole is created using a special tap . The insert is over-sized so that it anchors itself into the hole. Some have tangs to enable convenient install
but some do not. Special tools are required to install the inserts. When the insert includes a tang , it is snapped off
after installation. The insert can be configured to provide a thread locking duty.
The resulting female threads are strong because the flexibility of the insert provides an even distribution of
loads throughout the length of thread engagement. This flexibility also compensates for variation in
the formed thread allowing each coil to carry its share of the load. The limitation on length of a convenional
thread are overcome with this component and the load can be distributed over thread lengths far in excess of
that in a tapped hole with no insert.
The heli-coil internal profile is hard and polished dramatically reducing thread wear.
|
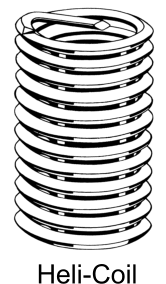
Heli-coil Catalogue
|
Table showing lengths (in nom.dias) of Heli-coil (Material Spec: AS7245) required to match
the screw strength of the material of the female thread with the screw strength
parent metal
MPa | Screw Ultimate strength (MPa) |
| 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 800 | 1000 |
| 70 | 1,5 | 2 | 2,5 | 3,5 | - | - |
| 100 | 1 | 1,5 | 1,5 | 2 | 2,5 | 3 |
| 150 | 1 | 1 | 1,5 | 1,5 | 2 | 2 |
| 200 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1,5 | 1,5 |
| 250 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1,5 |
| 300 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1,5 |
| 350 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1,5 |
|
Threaded Bush Insert
This is simply a bush which is threaded internally and externally. They are simple to install
require no special installation tools and do not require special taps. Some types incorporate Loctite
thread adhesive in the external thread. As with the helical wire inserts these components enaable
use of steel bolts with high preload forces with female tapped holes in a comparatively weak material.
They can also be used to repair damaged threads.
A typical threaded insert bush type is the
E Z Lok
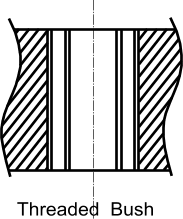
Shouldered Bush Insert
An engineered bush provided with a shoulder and internal thread. The bush is pressed in from the side opposite to the joint
face such that it is prevented from movement by the shoulder. This component would include features which prevent
rotation such as adhesive or knurling. This provides a very convenient and easy to engineer solution
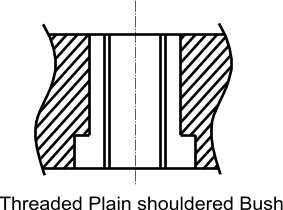 > >
|


 >
>