Chemistry Index Chemical Reactions
|
Reactions Chemical reactions are the heart of chemistry. A chemical reaction is when one
or more substances are changing into other substances. Chemical reactions are
evidenced by the disappearance of characteristics of the starting substances and
the appearance of new properties that identify the products; Reactions are identified in chemistry using simple equations. An example reaction equation, of iron reacting with oxygen in the corrosion process, is provided below;
The reactants are shown on the left of the equation and the products are shown on the
right. The number of atoms
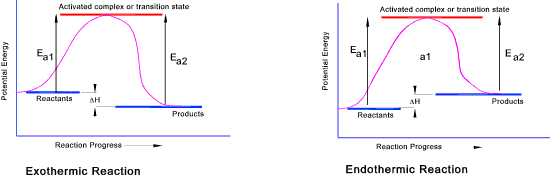
of each element will therefore be the same on both sides of the equation. A reaction can be exothermic (exoergic) or endothermic (endoergic) or for very rare cases athermic (aergic).
There are four basic types of reactions.
Types of Reactions The main types of reactions are:.. Oxidation- Reduction This is typically a reaction where one chemical is oxidised
and another is reduced i.e one chemical gains oxygen and the other
loses oxygen. This definition has developed into a more general view
of the process in which oxidation is the loss of electrons
and reduction is the gain of electrons.
Ref. Oxidation - Reduction Acid Base A reaction between an acid and a base to form a salt and water as the only products. A typical Acid- Base reaction is that between reactants Sulphuric acid and potassium hydroxide resulting in products potassium sulphate and water i.e. H2SO4 + 2KOH --> K2SO4 + 2H2O More notes are found on webpage Acid and Bases Acid - Metal Oxide A reaction between an acid and a metal oxide forms a salt and water as the only products. Acid - Metal A reaction between an acid and a metal, forming a metal salt and hydrogen as the only products. Acid - Carbonate A reaction between an acid and a carbonate forming a salt, carbon dioxide and water as the only products. Esterification A reaction forming an ester. Usually this is a reaction between an organic acid and and an alcohol forming an ester and water as the only products. Ref Organic Esters Hydrolysis A reaction where reactants water and a larger molecule are split into
two smaller product molecules, one of which has the hydrogen from the water and
the other has the OH group from the water. Hydrogeneration A reaction where hydrogen is added across a double bond or even a triple bond. Example Ethene and hydrogen --> ethane CH2=CH2 + H2 ---> CH3CH3 |
Relevant links..
|
|